
In this article, we will compare two of the emerging blockchain networks – Cosmos and Polkadot. We constantly see the increase in the number of blockchains that can challenge the Ethereum network, and Cosmos and Polkadot are definitely in that category.
The main purpose of Cosmos is to create “an internet” of blockchains so that networks can operate with each other easily. The native token of the Cosmos network is ATOM. On the other hand, Polkadot has pretty much the same goal – to make more blockchains connected. Today, Polkadot connects over 100 chains and can process up to 1 million transactions in a second.
Without further ado, let’s jump into details.
What you'll learn 👉
What is Blockchain Interoperability?
I would first like to define the term Blockchain Interoperability. Blockchain is a network with a database kind of operation while interoperability is an execution of several operations among the same kinds. So, we can then say that Blockchain Interoperability is a system of operations between two or more Blockchains.
Interoperability supports blockchains to share and easily access their data and operate with one another. The system through which blockchains share and “communicate” with each other is called blockchain interoperability.
Use Cases of Polkadot vs Cosmos
Even though both networks have the same goal (to connect multiple blockchains with each other), there are differences in their use cases. While Polkadot is focused more on security, Cosmos’s focus is more on adoption.
Furthermore, Polkadot is also focused on the loan market. The Centrifuge is the biggest project on Polkadot that aims to make more loans on the network. Cosmos Network is looking to incorporate business into the chain with the IRISnet project. The goal of the project is to provide business tools into the platform that will connect with users and increase efficiency. It utilizes a unified service model to improve business functions. It was created on Cosmos SDK.
Why Build A New Blockchain?
In general, there are two reasons why somebody can decide to build a new blockchain from scratch rather than build the application as a smart contract on one of the existing networks.
The first reason is related to the flexibility and customizability that your project needs. For instance, if your project requires a hash function, it will be costly to build it on the Ethereum network because of the gas fees because the function needs to be executed on the EVM each time.
The second reason is related to sovereignty. If you want to build an app on the existing network, you will have to follow the rules and protocols of that network. This could lead to various issues such as not pleasant user experience due to block times and gas pricing and state-changing decisions such as chain rollbacks.
5 Differences between Cosmos & Polkadot
Difference #1: Local vs Global Security
Cosmos and Polkadot work on two completely different models. Polkadot works as shown below:
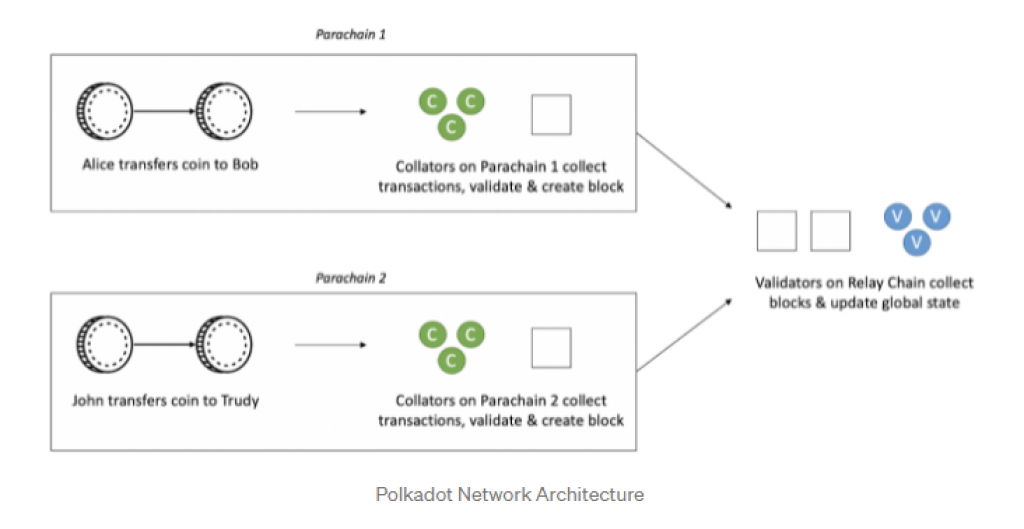
Parachains are in fact blockchains in the Polkadot network. You can look at each parachain at essentially an independent state machine that is able to utilize all sorts of unique functionality, consensus algorithm, transaction cost structure, etc.
When you look deeply into the Polkadot network, you will see that in fact all the parachains are children and their parent is called the Relay Chain. Relay Chain represents a “global state” of all the parachains combined. GRANDPA consensus is the consensus algorithm that Relay Chain uses to finalize blocks on the parachains rapidly.
On the other hand, the architecture of the Cosmos Network is much different, as shown below:
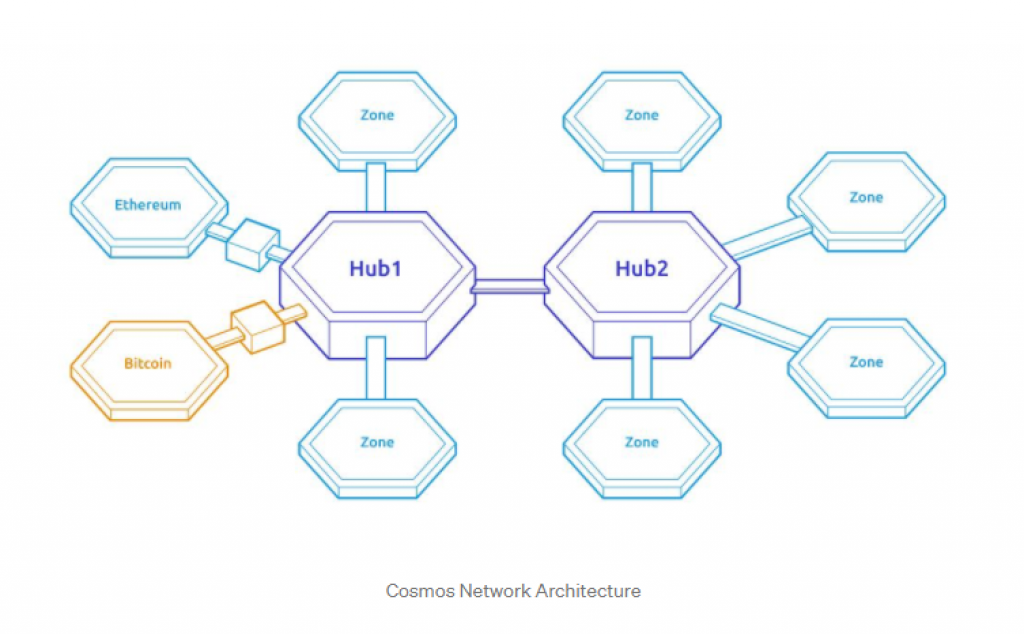
Polkadot uses a global model for security, while in the Cosmos Network, every (block)chain is independent and it secures itself. Each blockchain has its own consensus and its own validators that are responsible for securing that blockchain.
Difference #2: Governance & Membership
The second huge difference between Polkadot and Cosmos is related to governance and membership. As mentioned in the previous section of the article, in the Polkadot network, there is one Relay Chain and a number of parachains that are supported by the validators of the Relay Chain. As per the current estimate, there will be 100 slots for parachains, but I believe this number can be lower or higher in the future.
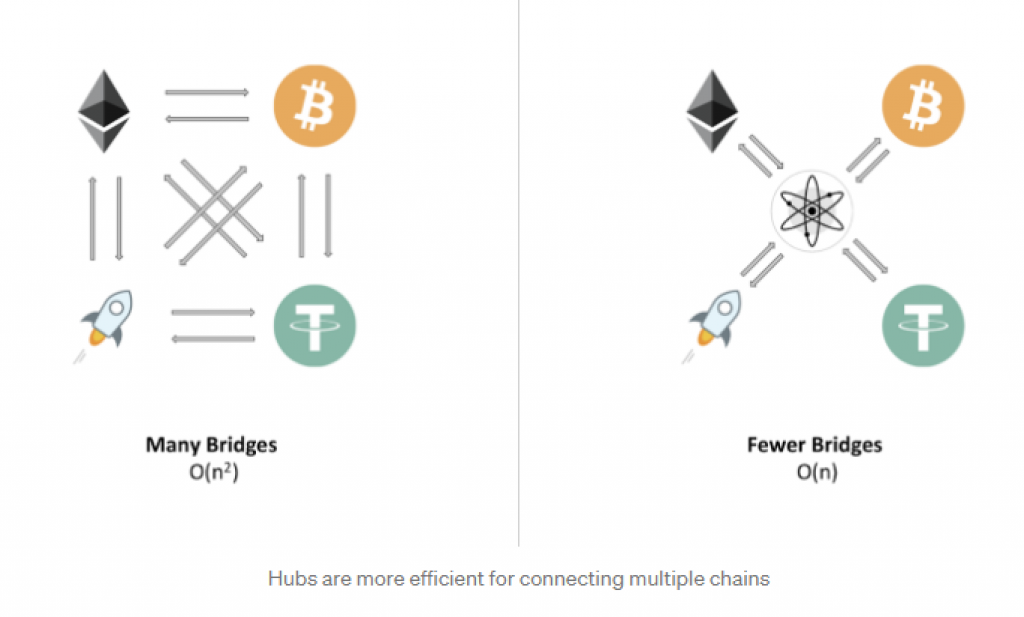
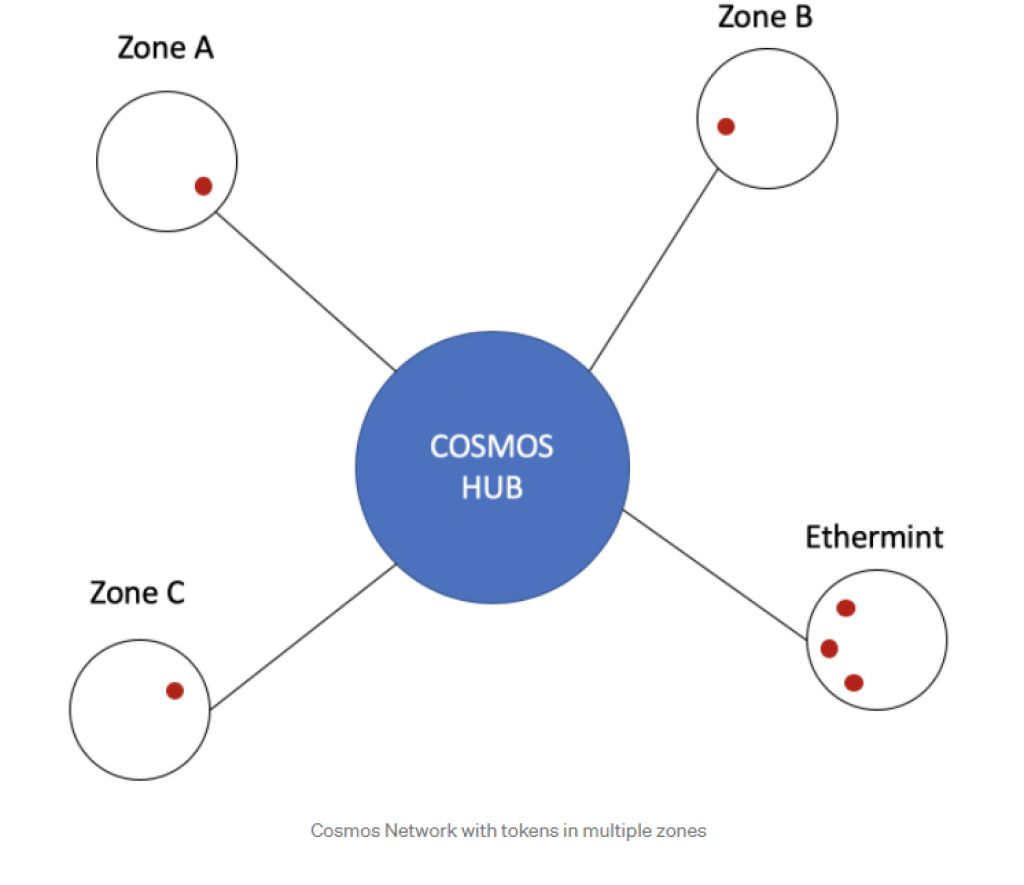
On the other hand, the Cosmos network has no rules of membership – literally, anyone can build a hub (or a zone). Hubs are blockchains themselves that have the goal to connect a group of other blockchains. If you want to look at some examples of hubs, probably the best ones are the Cosmos Hub that was launched in 2019 by the Tendermint team, and the Iris Hub which aims to connect various blockchains operating in China and Asia in general. Hubs are efficient in connecting multiple blockchains, as shown below:
Difference #3: Inter-blockchain Communication
Yet another big difference between Polkadot and Cosmos is their communication between blockchains and their goals. Polkadot is primarily focused on the arbitrary message that should pass between parachains. In the reality, this means that for example Parchain A can call a smart contract inside Parachain B and can transfer a token between them, or have any other type of communication. Cosmos Network focuses on transferring assets between chains which seems like a simpler method.
One of the biggest challenges in inter-blockchain communication is how to handle the situation where the chain that the data originates from recognizes to exclude the transaction. It is easier for Polkadot to share messages since this network uses shared security for all chains. Furthermore, Polkadot uses the “Fisherman” method – “bounty hunters” in the network that watch all chains and look for malicious activity.
Cosmos network uses a completely different method – since each chain has its own validators, it is easily possible that there are zones that are not good for colluding validators. In the real world, this means that when zone A wants to communicate with Zone B, Zone A needs to trust the Cosmos Hub and validators in Zone B. It sounds much more inefficient than the method Polakdot uses.
Difference #4: Consensus Algorithms
The next difference between Polkadot and Cosmos is the fact that they use different consensus algorithms.
Polkadot’s Relay Chain uses a consensus algorithm created by the team called GRANDPA. This algorithm actually allows the Relay Chain to control many blocks pretty quickly and accommodate a great number of validators, over 1000, since all the validators do not need to vote on every single block. Instead, validators vote on a single, highest block they presume is valid, and the consensus algorithm applies the vote to all validators in the block.
👉 On the other hand, each chain in the Cosmos Network uses any consensus algorithm that works under a certain specification that is called the ABCI spec. ABCI spec is created to control and standardize communication between the chains. Tendermint algorithm for example fits into this spec, but there are other consensus algorithms that can fit as well. The negative side of Tendermint is the overhead between validators – it can work very fast with 200 validators, but much slower with 2000 for example.
Difference #5: Substrate vs Cosmos SDK
Polkadot and Cosmos offer a complete software development system called Substrate (for Polkadot) and the Cosmos SDK (for Cosmos). The purpose of these kits is to allow developers to easily start building their own chains and include various modules such as governance modulus, authentication modules, staking modules, etc.
However, the big difference between these two is that the Substrate supports any language that is compatible with WASM (Web Assembly) while Cosmos SDK supports only the Go language which means that the former gives way more flexibility to developers. Since both networks are still relatively new in the blockchain world, I do expect them to add more features and languages in the upcoming years.
Conclusion – So, What’s Better: Polkadot or Cosmos?
To be honest – this is a million-dollar question as of today (February of 2022). If I have to give a vote to one blockchain, it would most likely be Cosmos. It is mainly because it offers more usability at the moment since it allows literally anyone to create projects on the network. However, we will closely watch Polkadot, since this network offers much more security and can more easily solve the problem of interoperability.
Note: Keep in mind that these are only our opinions based on my thorough investigation of the Polkadot and Cosmos networks. In any case, please do your own research before deciding which one to use.
At this point, it is good to note that all opinions and suggestions written in this article are not considered financial advice.
Please read our full review of the best projects on the Polkadot network and the best projects on the Cosmos network as well.
Read also:
- How To Stake Polkadot on Polkadot.js, Ledger, Binance, Crypto.com
- What is Polkadot?
- Solana vs Polkadot
- Importance of blockchain interoperability
- Best Cosmos Wallets
- How To Get Cosmos Airdrops?
- How to Stake Cosmos
- What are Parachain Auctions and Crowdloans on Polkadot?
- Ethereum to Cosmos Bridge
FAQ
Let’s look at some frequently asked questions when it comes to Polkadot and Cosmos networks.
Is Polkadot or Cosmos better?
As mentioned above, my vote would probably go to Cosmos but it is a very close call. The goal of the Cosmos network is to allow separate blockchains to communicate with each other in a seamless manner. Polkadot focuses more on security, while Cosmos Network focuses on adoption.
Is Cosmos ATOM A Good Investment?
Cosmos has certainly performed very well over the past 12 months (article written February of 2022), shooting up in value. That said, please do be cautious. You will need to do your own research and never invest more than you can afford to lose.
What are the best exchanges to buy ATOM?
ATOM is one of the most popular coins in the crypto world. You can buy it on various exchanges such as Binance, Gate.io, Uphold, Coinbase, KuCoin, BitYard, and Huobi Global.
Can Cosmos Polkadot coexist?
Cosmos and Polkadot are considered leaders in blockchain interoperability and real challengers to the Ethereum network. Even though you can look at them as competitors, they have the same purpose in the crypto world, so I can safely say they might coexist – just look at Visa and Mastercard in the credit card industry.
Is Cosmos a Layer 2?
Yes, it is. Cosmos aims to provide effective scaling solutions for all layer-2 projects and it actually achieved this by having interoperability as its core purpose.






Here’s the thing with Polkadot, it markets itself as a layer 0 network interoperability layer for blockchain. But looking at this model of parachain auctions for 100 slots, a defi project will get a lease for 2 years to which after then it will have to go through the same lengthy and risky process and effort to renew their lease evey 2 years and hope the community and market sees something valuable to further themselves just so they can exist on the network. As a defi project, why have this existential risk hanging over their head every 2 years when they can develop less expensively with less restrictions without a “landlord who holds all the keys” on other network defi eco systems like cosmos. I don’t think polkadot a practical model for defi projects wanting more independance and control to run and exist, they will want to connect across many other blockchains with less restrictively other than just going through polkadot. But to reframe it, rather than being THE layer 0 network for everything, I think the role of polkadot could make a good blockchain to facilitate crowdloan fund raising for new defi projects, acting like an temporary INCUBATOR ecosystem, so to say, it’s role as a place to fund and grow new projects before they branch out into other better modern blockchain ecosystem models.