What you'll learn 👉
What is the cryptocurrency tax rate?
If you’ve earned crypto through activities like trading, mining, or staking, it could be subject to taxation as either long-term capital gains or ordinary income. Here are some things to know about each type of taxation.
Ordinary Income
Earning crypto through activities like mining or staking is treated as ordinary income for tax purposes. Depending on one’s financial situation, this can be anywhere from 10% to 37%.
Long-term capital gains
The long-term capital gains tax rate applies if you’ve owned the crypto for more than a year. Depending on how much money you make, this can be anything from 0% to 20%.
Short-term capital gains
You’ll have to pay the lower short-term capital gains rate on any profits you make from selling crypto that you’ve had for less than a year. A person’s tax rate on this amount might vary from 10% to 37%, depending on their other taxable income.
How are crypto taxes on capital gains determined?
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) says that the length of time that you hold crypto determines how much capital gains tax applies. Short-term capital gains tax applies when you hold crypto for less than one year. Long-term capital gains tax is applicable when you hold crypto for one year or longer.
If you’re trading crypto for profit, you’ll owe capital gains tax based on the difference between the price you originally paid for your crypto and the current market value. You must report capital gains on Form 8949, Schedule D.
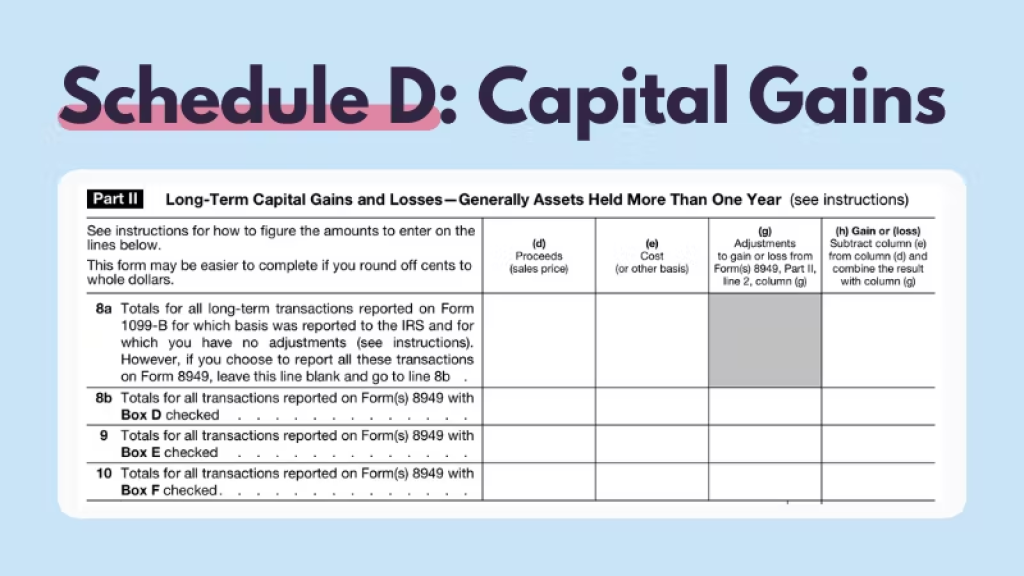
Short-term capital gains
Short-term capital gains are taxed at the same rate as ordinary income by the federal government, which can range from 10% to 37% of your total income.
As you can see in the table below, for example, you make $100,000 in income and $20,000 in short-term crypto investments. Your income is $120,000, which means that you have to pay taxes on that. The first $10,275 will be taxed at 10%. Taxes of 12% will be applied to income between $10,275 and $41,775. The tax rate is 22% on money made between $41,775 and $89,075. A 24% tax would be due on the remaining $30,925.
| Rate | Single | Married couples filing jointly | Head of household |
| 10% | Up to $10,275 | Up to $20,550 | Up to $14,650 |
| 12% | $10,275 – $41,775 | $20,550 – $83,550 | $14,650 – $55,900 |
| 22% | $41,775 – $89,075 | $83,550 – $178,150 | $55,900 – $89,050 |
| 24% | $89,075 – $170,050 | $178,150 – $340,100 | $89,050 – $170,050 |
| 32% | $170,050 – $215,950 | $340,100 – $431,900 | $170,050 – $215,950 |
| 35% | $215,950– $539,900 | $431,900 – $647,850 | $215,950– $539,900 |
| 37% | $539,900+ | $647,850+ | $539,900+ |
Long-term capital gains
If you held the crypto for a period longer than one year and then opted to sell it or trade it, long-term capital gains tax rates will apply to your earnings. Long-term capital gains tax has much lower rates than short-term capital gains, motivating people to invest their money over the long haul.
As you can see in the table below, for example, you make $100,000 in income and $20,000 in long-term crypto investments. Your income is $120,000, which means that you have to pay taxes on that. The first $41,675 will not be taxed because the tax rate is 0%. A 15% tax would be due on the remaining $78,325.
So, for $20,000 in long-term crypto investments, you will be taxed at the 15% rate, which is $3000. On the other side, for $20,000 in short-term crypto investments, you will be taxed at the 24% rate, which is $4800. As you can see, you would be saved $1800.
| Rate | Single | Married Filing Jointly | Married Filing Separately | Head of Household |
| 0% | $0 – $41,675 | $0 – $83,350 | $0 – $41,675 | $0 – $55,800 |
| 15% | $41,675 – $459,750 | $83,350 – $517,200 | $41,675 – $258,600 | $55,800 – $488,500 |
| 20% | $459,750+ | $517,200+ | $258,600+ | $488,500+ |
What crypto transactions are taxable?
Any time you earn or lose money is considered a taxable event. You must disclose every taxable event that has an impact on your bitcoin investments on your tax return.
There are two types of taxable events related to crypto:
- Income tax
- Capital gains tax
Because of the varying tax treatment, knowing which events fall into each category is crucial.
Selling cryptocurrency for fiat currency
If you buy crypto, you might want to consider selling it again for cash. This could help lower your taxes.
For example, let’s say you bought ETH for $2,000 in October, then sold them for $3000 in December. You’d report a short-term gain of $1000, which would be subject to income taxation. But if you bought ETH for $2,000 in November and sold them for $1500 in January. In this case, you’d report a short-term capital loss of $500 and reduce your taxable income. So, you can use this strategy to minimize your taxes.
The term “tax-loss harvesting” refers to the practice of selling crypto assets at a loss in order to offset future capital gains.
Using cryptocurrency to buy goods or services
Assume you purchased 10 LTC for $10 each before 2013 and haven’t touched them since. You used one LTC to buy a new hard disk for $65, the price of one litecoin at the time of purchase.
As a result of this exchange, you have created a taxable event. Therefore, you made a long-term capital gain of $55, which is the difference between the $10 cost of purchase and the $65 market price of the litecoin at the time of sale.
Your transaction is a long-term capital gain.

Swapping or trading one crypto asset for another
Whether traded directly between peers or on a crypto exchange, swapping crypto assets is regarded as a taxable event.
For instance, you paid $1000 for 5 ETH. You swapped 5 ETH coins for 1 BTC for $10,000. The $9000 capital gain, or the difference between the purchase price and the trading price of ETH, is realized at the time of your swap. You must declare $9000 as a capital gain.
When transferring the same assets between exchanges or wallets (i.e., you move your BTC from Coinbase to Kraken), there aren’t any tax implications, that is, no gains or losses are incurred.
Mining
You earn crypto through mining, you must report it as income. The fact that you mined the digital currency makes its value realized, that is, you didn’t need to sell it. So, you must pay income tax immediately for the whole mined amount.
Staking
Staking involves several different transactions. Each transaction determines how your crypto is taxed. Of course, where you live plays a major role as well.
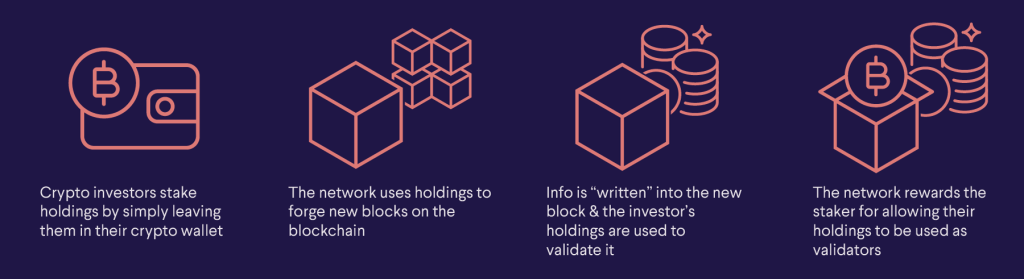
Any time you move your coins or tokens to a staking pool, wallet, or third-party staking provider, you do not expect this to be a taxable event. To put it another way, it is the same as moving your own crypto from one wallet to another.
Whether or not you must pay taxes on your stakeing rewards is determined by the laws of the country in which you reside. In most cases, the income tax you pay on staking rewards will be calculated using the coins’ market value when you receive them. When you sell, trade, or spend your staked coins, you will be subject to Capital Gains Tax.
Airdrops
The IRS regulations specify that the value of an airdropped asset at the time the recipient obtained ownership must be included in their taxable income as ordinary income. Therefore, you are required to have any tokens obtained through airdrops in your taxable income.

Any appreciation in the value of the airdropped asset, from the moment you acquire it to the moment you discard it when selling, swapping, or trading, is subject to capital gains tax.
The question is, does the airdrop become taxable when it is claimed or when it is deposited into the wallet? A change in reporting dates can have a significant impact on the amount of income an investor must report. We advise discussing this with a crypto tax accountant.
How can I reduce my crypto capital gains taxes?
Whenever possible, you should invest in cryptos for the long term to minimize your tax liability.
Using crypto tax software, you can select from four distinct unique ID accounting strategies: FIFO, LIFO, HIFO, and Minimization.
Long-term trading should be prioritized wherever possible, which frequently results in lesser crypto capital gains on tax returns.
It is possible to lower your tax burden by using tax loss harvesting. Zenledger is good for this as they have a separate tool only for this.
Capital gains vs. income tax events
The IRS defines a Capital Gain as “the difference between the amount you paid for something and the amount you sold it for.”
Income taxes are based on how much money you make during the year, so there is no way for you to pay fewer taxes without reducing your income.
Capital gains events
This is a list of Capital Gains events:
- selling your crypto for regular money,
- making a crypto exchange,
- making purchases with crypto.
Ordinary income events
This is a list of Ordinary Income events:
- gaining crypto as a reward for referring a friend,
- the process of receiving crypto from an airdrop,
- gains in crypto interest,
- receiving a paycheck in crypto,
- gaining crypto by staking or mining.