Blockchain technology has often been lauded as the “killer of intermediaries”, removing the need for third party financial and banking services. The increased verticalization of blockchains has led to the technology becoming applied in various industries and areas. However, this has perhaps exacerbated the already obvious need for intermediaries, which exists even in the world of crypto. As blockchains are created for various means, they do solve many internal issues. But their main problem remains the fact that they are unable to communicate with one another directly. Often times people want to transfer one cryptocurrency into another; this is impossible without the help of an intermediary like an exchange.
This is why blockchain enthusiasts and developers started working on a new concept called interoperability projects. Interoperability is the ability to easily share information and transact across blockchain systems. In a fully interoperable environment, if a user from another blockchain sends you something on your blockchain, you will be able to read, comprehend, and interact with or respond to it with little effort. Such projects look to create a platform that will enable various different blockchains to communicate freely with each other, without the need for an outside intermediary. Craig Sproule, founder and CEO of Crowd Machine, recently said the following in an interview with Forbes:
“At the moment, interoperability is managed at the app level, but that requires developers to be proficient in different smart contract languages, Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) or third party tools. If the interoperability requirement is to continue to be resolved within the app, then an approach would be to standardize on a common smart contract language across all blockchains.”
Standardization does seem like a good approach that has shown its value in numerous other industries. Having the basis set and already developed will spare new projects a lot of time and resources, and will ultimately create an environment where projects are free to interoperate freely. Interoperability lowers the entry costs into the blockchain industry and raises the security bar by making the entire network more robust. It also helps end users manage their funds in a simpler manner. Identity wallets like Civic or Metamask are currently individual and unable to communicate with one another; in an interoperable world a user will be able to access both with a single identity.
Bitstamp is one of the oldest cryptocurrency exchanges. Read our Bitstamp review here.
As I’ve already pointed out, there are a couple of projects out there that are trying to create a bridge between the various blockchains that are available on the crypto markets. The most famous ones to date are as follows:
AION
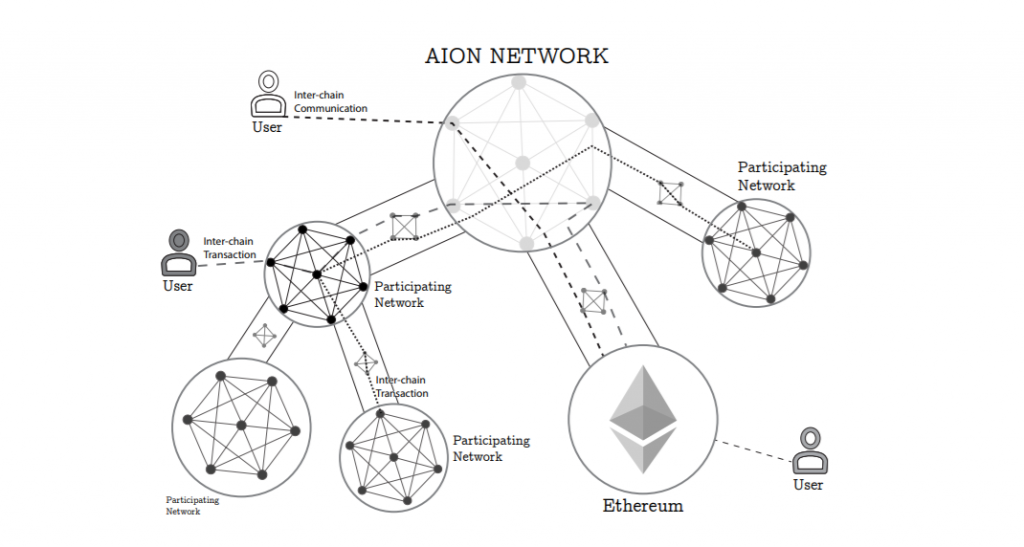
Aion is a third-generation protocol looking to provide blockchain interoperability for any public or private blockchain. Aion lets users federate, scale and spoke in a safe, fast and transparent way. The platform facilitates inter-blockchain communication and transfer of value/data by employing a high-performance bridging mechanism. It has a high performance virtual machine which runs dApps and allows them to communicate with dApps on other blockchains. Finally, it lets developers add custom features to their blockchains (like different algorithms and virtual machines) without sacrificing interoperability.
Aion network allows multiple blockchains to exist and at the same time lets users move value and logic across said blockchains, eliminating the need for intermediaries. And the platform has already set the wheels in motion to fulfill its ultimate purpose. It is currently a member of the aptly-called Blockchain Interoperability Alliance, where a conjoined effort is being made alongside ICON and Wanchain to create an ecosystem of interoperability. Aion-compliant blockchains refer to the participating blockchains that comply with the Aion protocol; said blockchains will allow for bridges to be established easily to forward interchain transactions through Aion-1. To be Aion-compliant, a blockchain must meet certain requirements:
- Be decentralized in some fashion and support procedures commonly found in blockchains such as atomic broadcast and transactions.
- The exact implementation is left to the discretion of the bridging protocol and the network itself.
- Be able to recognize interchain transactions as distinct from regular transactions.
- Be aware of the consensus protocol used by the bridge and store a transaction deemed valid.
- Implement locktime or a similar feature that allows tokens to be held by the network for a period of time.
So the platform will require a certain degree of standardization. More specific details on the requirements will be published as the project progresses.
Polkadot
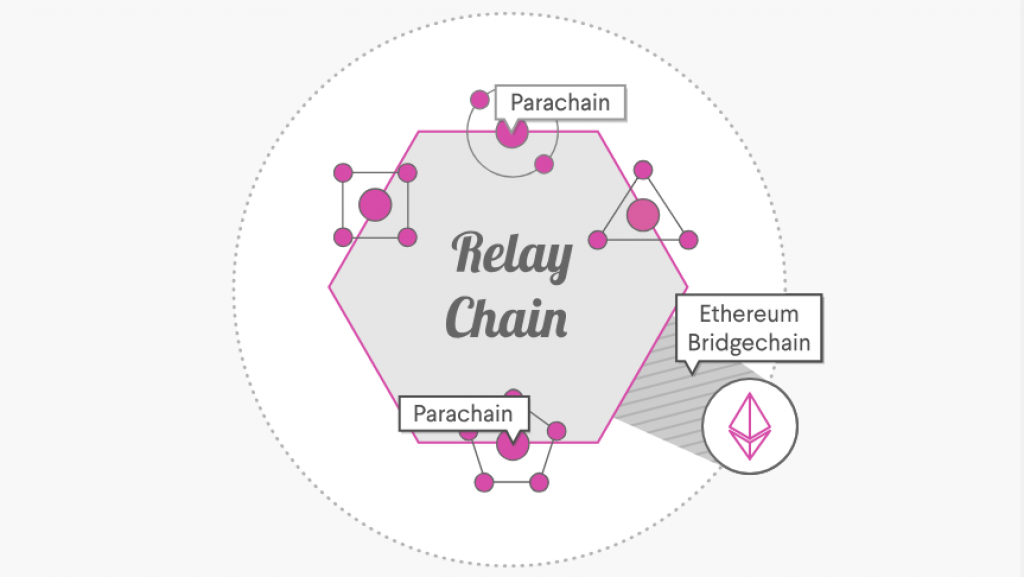
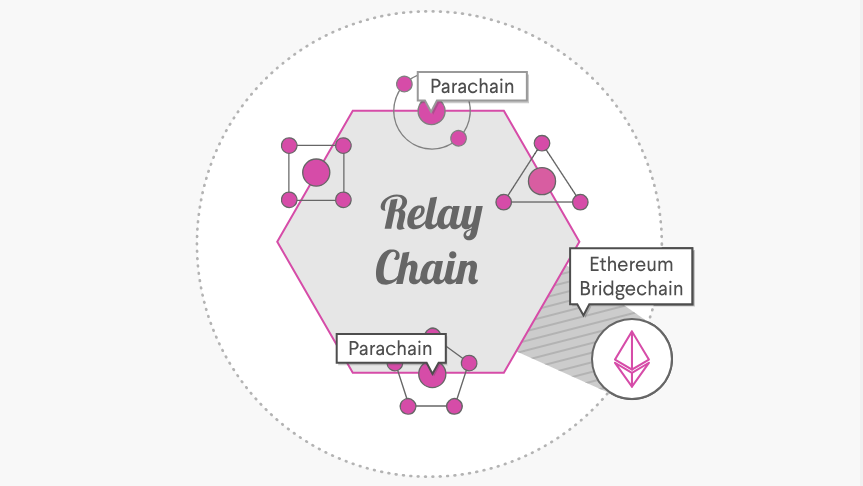
Polkadot network is one of the newest and best received interoperability projects out there, considering the fact that they’ve completed a $140 million USD ICO to fund their ongoing efforts. Calling themselves a “heterogeneous multi-chain technology”, the network will utilize multiple customizable parachains that will allow Polkadot to achieve impressive levels of scalability. It will also have a relay chain to coordinate consensus and transactions and bridges that will serve as links to outside blockchains. The platform wants to lead the world into what they call Web3: a decentralized internet for everyone.
HitBTC is one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges. Read our HitBTC review here.
Polkadot is built to connect private/consortium chains, public/permissionless networks, oracles and future technological developments yet to be created in the Web3 ecosystem. It enables an internet where independent blockchains can exchange information and trust-free transactions via the Polkadot relay chain, with the key tenets of scalability, governance and interoperability. Each of these elements is seen as a dot, and Polkadot intends to connect them to create an ecosystem designed to distribute power and equity.
It uses the DPoS algorithm that will have validators and nominators in charge of governance, which can lead to a degree of centralization down the line. It will also have collators who will maintain the parachains by collecting transactions from users and producing state transition proofs for validators. Final layer of the network will be fishermen, who will monitor the network and prove bad behavior to validators. Projects roadmap has its genesis block planned for 2019, which is when we can expect the interoperability blockchains to start seeing general adoption.
Ark
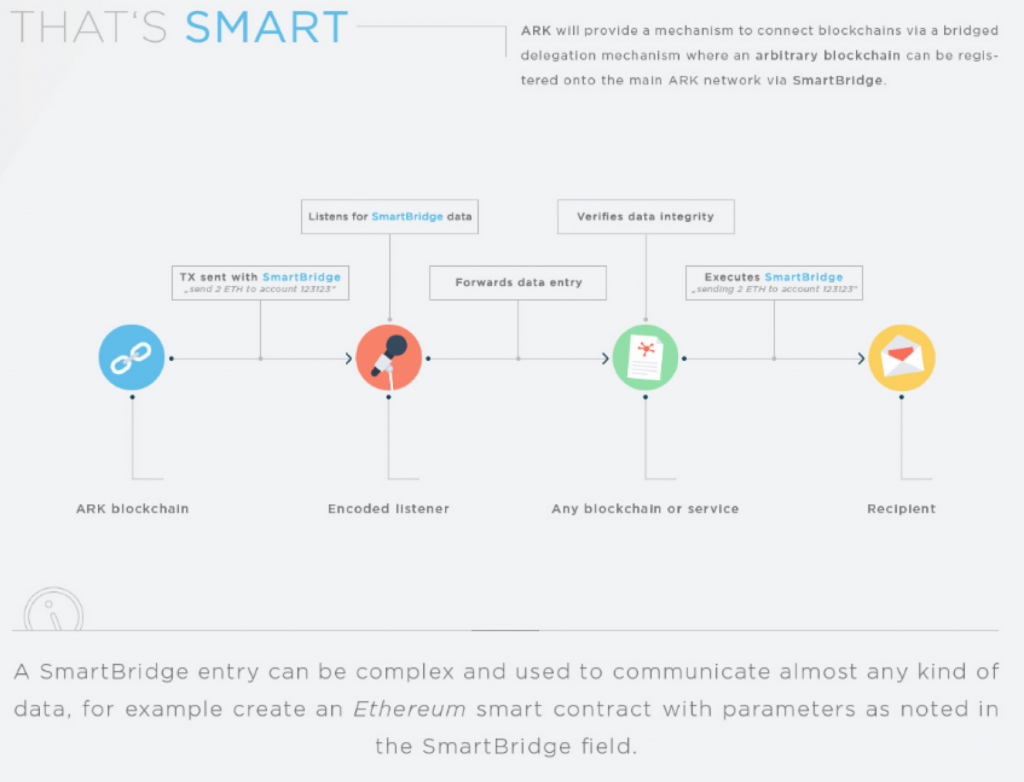
A French project looking to break into the interoperability market, Ark wants to create an ecosystem of linked chains and a virtual web of endless use cases which will make the platform flexible, adaptable and scalable. It will simplify the communication between blockchains by being an “all-in-one blockchain solution” capable of bridging the gaps between other cryptocurrencies.
Born from the minds of the creators of Lisk, Ark utilizes SmartBridges technology to create the interoperable ecosystem which will allow currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum etc. to directly communicate. Their website claims Ark’s Core is configured to produce ultra-fast transactions with 8 second block times which is much better than what Bitcoin, Ethereum or any other altcoin can achieve.
The coin uses an EOS-like DPoS for governance which is a bit less centralized, with 51 delegates regularly voted for block producer responsibilities by the community. Every token holder in the ARK community has a proportionate voice in the decision-making process. ARK currently supports Python, Ruby, Java, Elixir, and other programming languages.
Cosmos
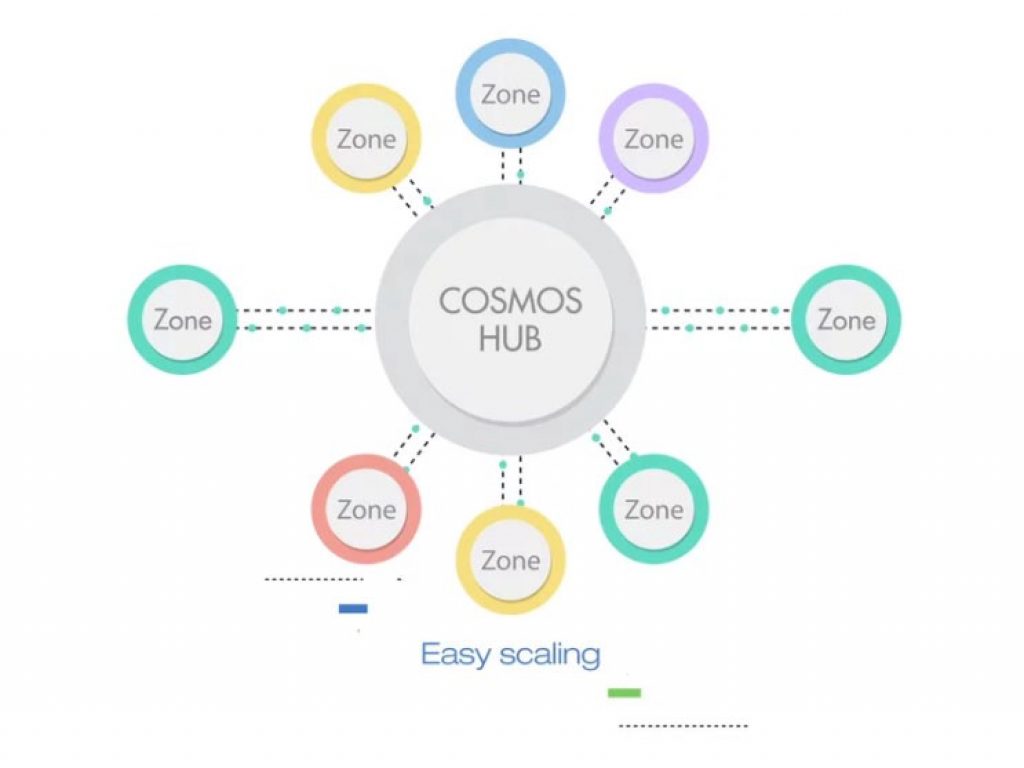
Cosmos is another “blockchain of blockchains”, a network capable of supporting multiple independently functioning parallel blockchains. Cosmos is an open, permissionless network that will allow anyone to build blockchains on top of it. The platform will focus on creating an interoperable experience for multiple blockchain networks by utilizing a native underlying blockchain layer called Cosmos Hub. This hub will connect to other zones in the Cosmos Blockchain Network via a unique inter blockchain communication protocol, called IBC. The Cosmos hub keeps a record of the total number of tokens in each zone, making it possible to transfer tokens between zones quickly and easily without the need for third-party liquid exchange, which adds extra transfer costs.
You can choose the best coin exchange by reading this article. Read here how you can quickly convert other coins to bitcoin and the other way around.
Cosmos will have 4 main parts: Hub, Zones, Validators and Atoms. The hub is the basis blockchain that enables Zones to interoperate and function together. Each zone is an independent blockchain built on top of the Hub, powered by Byzantine fault-tolerant consensus protocols like Tendermint. Some zones act as sub-hubs, having several other zones that interoperate through them. Cosmos network will connect multiple zones through the IBC protocol, enabling various cryptocurrencies to communicate. If the network becomes overwhelmed with transactions, a new zone can be created to relieve the pressure and double the total zone throughput.
Validators are an important part of the platform’s Proof of Stake algorithm. Each user needs to stake his Atom coins, the currency of the platform, in order to become a validator. The amount of coins staked gives you proportional voting power. Malicious validators therefore place their holdings on the line and risk using everything if they start behaving in a network-unfriendly way. Finally, The Atom token is the native asset to the Cosmos Hub, which can be used across the different distributed ledgers of each zone. Atoms give users the right to vote, validate, or delegate to other validators. Like Ethereum, the Atom token is considered to be the gas for paying for transactions.
In conclusion…
Interoperability will be an important milestone for the future of blockchain. Once it happens, many new horizons will become unlocked for the cryptocurrencies on the market. Faster and cheaper transactions, increased scalability and network throughput, safer data and value storage will all be crucial in creating the much lauded and blockchain based Internet of the future.





