What you'll learn 👉
Table Of Contents
Quantstamp is an upcoming protocol with the goal of auditing the security of smart contracts, as that remains somewhat of a problem these days.
Smart contracts are a potentially revolutionary advancement in technology and it is evident the concept of smart contracts is well appreciated by developers all over the world. However, that doesn’t mean all implementations of this technology are successful, and, in fact, one simple flaw can cause the contract to fail, leading to disastrous consequences for users. In fact, over the past couple of months, there were a fair few issues with smart contracts, all of which could have been easily avoided. In June, 2016, $55 million worth of Ethereum was stolen due to a bug in the smart contract and. Also, in 2017, $30 million was stolen due to a one-word error in the contract code. Securing smart contracts is essential for mainstream adoption of Ethereum and the cryptocurrency space in general, but this has proven to be far more difficult than people realize.
There is definitely a demand for smart contracts, with the aim of making them more efficient, fast, dynamic and client-focussed, and this is where Quantstamp comes into the picture. The potential of this project could be huge, even though it remains to be seen how its efforts will fare in the long run.
In this extensive review, you will find out how Quantstamp works today.
What is Quantstamp?
Quantstamp, found online at Quantstamp.com, is a security audit protocol designed to find vulnerabilities in Ethereum smart contracts such as those which led the DAO failure in 2016 or recent parity wallet hacks. Over time, Quantstamp expects every Ethereum smart contract to use the Quantstamp protocol to perform security audits and it has already demonstrated the demand for their platform with their recent smart contract audit of the Request Network ICO.
How Does Quantstamp Work?
Quantstamp is a specialized network that acts as a critical piece of transparency by enabling automated checks on smart contract vulnerabilities, and this network connects investors, developers, and users around a transparent and scalable proof-of-audit protocol.
The platform revolves around the use of Quantstamp tokens, which firstly, allow the network to operate in a decentralized way, delivering computation fees to verifier nodes and secondly, provide bounties in the form of Quantstamp tokens for identifying and reporting vulnerabilities.
The Quantstamp protocol consists of two parts, including:
- Automated Software – an automated and upgradeable software verification system that checks the smart contract code for flaw. The conflict-driven distributed SAT solver requires a large amount of computing power. However, it will be able to catch increasingly sophisticated attacks over time.
- Manual Checks – In the long-term, Quantstamp aims to allow for fully automated smart contract checks via their software that will reward human participants for finding errors in smart contracts. This system will bridge the gap while moving towards the goal of full automation, but until this becomes a reality, Quantstamp will be semi-automated. This means that they will use a combination of automated software combined with human participants that check the contracts manually and receive tokens as a reward.
The auditing process is the main focus of the Quantstamp project, so in this section we will focus on it.
The Auditing Process
If a developer wants to deploy a smart contract based on Ethereum, they can submit their code to be audited on the Quantstamp network to minimize the risk of losing funds due to security vulnerabilities. Depending on the size of the audit needed, the developer can choose how much bounty to send to the network i.e. how much financial reward they will pay for the auditing. The QSP network receives the request and QSP performs the validation required for the audit on the next Ethereum block.
A report is then produced which classifies the smart contract issues based on their severity, with 10 being a major vulnerability and 1 being a minor one.
Private or Public
When requesting an audit, the developer can choose to make the report private or public. This means that it is encrypted and only accessible by the developer or by anyone with access to the public network meaning anyone would be able to view it, respectively.
Is It Foolproof?
While Quantstamp does not guarantee 100% that the source code is flawless, it does provide a much higher degree of assurance that the code is secure by using both automated and crowdsourced methods.
The Quantstamp protocol relies on a distributed network of participants who use Quantstamp Protocol (QSP) tokens to pay for, receive, or improve upon verification services. These participants mitigate the effects of bad actors, provide governance, and provide the required computing power. Below are the different types of participants that will help the network to improve over time:
Software Contributors (Automated) – Quantstamp will need to upgrade their software in order to move towards a fully automated system. Most Contributors will be security experts and they will receive QSP tokens as an invoice for contributing software for verifying Solidity programs. All contributed code will be open source, which means that other members of the community will also be able to verify its validity.
Validators (Automated) – These individuals do not need security expertise as they simply run a node on the network. In other words, they contribute computer processing power and in return, they receive QSP Tokens.
Bug Finders (Manual) – The initial stages of Quantstamp will involve manual smart contract checks which will be carried out by bug finders, who will get paid in QSP Tokens for their work.
Contract Creators – These individuals pay in the form of QSP tokens in order to get their smart contract verified.
Contract Users – These individuals will have access to results of the smart contract security audits.
Voters – The governance system is a core feature of the protocol because it reduces the chance of upgrade forks and decentralizes influence of the founding team over time. Decentralises influence of the founding team over time via the governance system. This allows token holders to vote on system upgrades.
Does Quantstamp Solve Real Market Issues?
As I already said, smart contracts can have flaws and there have been a number of events over the last few years that have proved this to be the case. For example, in June of 2016, a hacker was able to exploit a bug that was contained in the DAO smart contract, and steal approximately $55 million in Ether.
Technically though, he didn’t steal anything because he actually followed the rules outlined by the smart contract, which in other words means that a huge amount was taken from investors due to an avoidable mistake in the smart contract. This was viewed by many as a loophole that was not corrected and it ultimately split the community and led to the creation of Ethereum Classic, an alternative project developed to maintain the original non-forked chain of Ethereum.
Problems like this one raise serious trust problems associated with Ethereum’s own smart contracts. This could result in distrust from the public, which could lead to slower adoption.
Quantstamp Solution
Quantstamp will provide a scalable method to audit smart contracts, which will be carried out manually but, in the long term, the project aims to allow for fully automated smart contract checks via their software. They are taking the first and most important step in ensuring that smart contract code is as secure as possible, and the result of this should be to avoid smart contract bugs, which should allow them to function correctly. Quantstamp aims to ensure that events like the collapse of the DAO do not happen again, and in return this should increase public adoption.
There is the rapid increase in the number of platforms being hosted on the Ethereum network, and about $3.2 billion are locked into smart contracts on the Ethereum network. This number will continue to grow as more and more smart contracts are deployed, so it would be an understatement to say that there could be a huge demand for this project.
Is the Quantstamp Token Price Going to Increase?
„Is the token price truly linked to the platform usage?“ is incredibly important question that people often overlook when investing in cryptos.
Investing in cryptocurrencies is not the same as traditional investing. When you purchase shares in a company, you essentially become one of the owners, which entitles you to certain rights. As a part-owner, you are eligible to a proportionate share in the company’s performance, and as the company makes increased profits, the share price will increase and your investment value will rise also.
With the majority of cryptos, the tokens don’t represent shares or real economic rights over the company that issues the ICO. This means that it’s possible for the company to be successful and yet the token prices may actually fall if they aren’t correctly linked to the platform usage.
Supply and demand on exchanges is the ONLY factor determining token price – like the price of gold increases or decreases based solely on supply and demand. Supply and demand are affected by many factors. However, the price moves up or down to the combination of these two.
The Sources of Demand
The demand for the Quantstamp platform stems from projects fixing many of the flaws seen with Ethereum smart contracts. With the rapid increase in the number of platforms being hosted on the Ethereum network, the demand for this is growing at a rapid rate, but this doesn’t automatically create demand for the token.
In the case of Quantstamp, projects can only make use of Quantstamp’s services through the purchase of QSP tokens (which are used to pay for, receive or improve upon verification services) via the exchange. There is massive demand in the marketplace for Quantstamp’s services today, and as more projects want to use Quantstamp’s services, the demand for the token will increase and so should the price as a result.
The Result?
The price of the Quantstamp token is sufficiently linked to the demand for the platform, which means that Quantstamp has successfully passed this test.
The Quantstamp Token Sale
Quantstamp tokens are ERC20-compliant Ethereum tokens, and Quantstamp issued a fixed supply of 1 billion tokens, meaning a zero inflation rate but this doesn’t mean that new tokens won’t enter the market though. A total of 65% of the tokens were sold during the ICO, 20% went the team and advisors, 10% to the core activities reserve, and 5% for community development.
The QSP team indicated that if the exchange price of QSP drops below the ICO price, they will buy back the tokens. For me, this is an indicator that the team is confident in their project.
The Team behind Quantstamp

QSP was founded by Richard Ma and Steven Stewart in June 2017. A team consists of eleven members (soon to be thirteen with the arrival of two new Senior Engineers) and eight additional advisors who are well poised to carry their vision forward. I think the team is very strong filled with all-stars, who come from strong universities across North America with a number of individuals holding PhDs.
Notable team members are:
- Richard Ma, CEO – He has experience as an algorithmic trading fund manager and he previously worked for s big companies such as Tower Research Capital and Palladion Capital. He has strong background in trading, software verification and general business management and he handled millions of dollars of trading using extreme software testing methods.
- Steven Stewart, CTO – Before he had even completed his undergraduate degree, he was hired by the Canadian Department of National Defence as a computer systems analyst and he worked there for five years. He previously founded Many Trees Inc that built GPU in-memory databases for ML.
- Vajih Montaghami, Senior Security Engineer – He has PhD from university of Waterloo and he is a man with experience as a software engineer at both Amazon and Google.
- Evan Cheng, Advisor – He was Apple’s Senior Manager for the LLVM Back-end Team for seven years before moving on to his current position as a director of engineering at Facebook. He also joined Cindicator advisory team and ChainLink, a decentralized Oracle network, as a Technical Advisor.
- Chris Miess, Advisor – The former CFO of TenX and the founder of Iconic Partners.
- Dr Vijay Ganesh, Advisor – A professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, at the University of Waterloo who was a research scientist at MIT, and completed his PhD in computer science from Stanford University in 2007.
- Min Kim, Advisor – A chief of staff at Civic that joined Quantstamp Advisory Board in September 25 2017.
Quantstamp Roadmap
Quantstamp was founded in June 2017 and in a short amount of time, they have achieved significant progress. They completed their first successful, semi-automated audit for 4 companies including Request Network just four months later.
Noteworthy milestones for the company’s future include:
- Building the Quantstamp validation node, which is an automated Ethereum node (January 2018)
- Deployment of the test network (April 2018)
- Release of the mainnet version 1 (August 2018)
- The addition of smart contract alpha product on the mainnet smart contracts (October 2018)
Quantstamp Selling Points
First Mover Advantage
With the recent surge of blockchain based startups and ICOs, there is a tremendous need for smart contract auditing, but Quantstamp is the only project we are aware of that are offering it at this time.
Coinbase Networking
Quantstamp recently pitched to Coinbase, which is one of the most valuable crypto companies in the sector. One could speculate a potential partnership between Coinbase and Quantstamp, where any newly added ERC20 Coins to Coinbase would need to be audited by Quantstamp, which could help facilitate Quantstamp’s position as the industry’s standard.
Growing Demand
The number of ICOs launched on the Ethereum blockchain is increasing each day, and with the rapid growth of the prevalence of smart contracts, and particularly those hosted on Ethereum, auditing platforms like Quantstamp could become increasingly important.
Barriers to Success
Although Quantstamp is currently positioned at 120th (not even in the top 100!) in the market, we are huge fans of it and we believe it is potentially one of the most undervalued projects in the market.
However, as investors, we always aim to be as critical as possible and search for barriers to success. That’s why we’ve highlighted a few potential hurdles to consider:
Trust/Adoption
Security of a smart contract is more important than any other software or piece of code, and Quantstamp claims that current smart contract security efforts rides on the belief that no bad actors are to be hidden within the company. However, their project involves trusting a system that has gone through limited testing because the team has only completed one security audit, which indicates there is still a lot of work to be done in this regard. However, with their recent smart contract audit of the Request Network ICO, Quantstamp has already demonstrated the demand for their platform. This also shows that the team is competent and that they have a working prototype in place.
Competition
Quantstamp should not face any direct competition. However, there are a number of companies that are focusing on smart contract creation and the lowering of costs involve, including Agrello, Etherparty and Blockcat, which are well known projects that have raised significant funds. Here is a table to compare them:
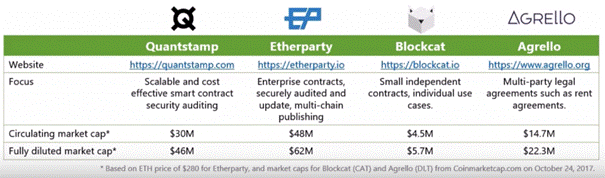
These competitors will begin to come into play if people are slow to trust the Quantstamp system.
Extra Points to Consider
Tier 1 Investors
A number of Quantstamp’s tier 1 investors agreed to a lock in period for their investments, which shows how many important players see the long term potential of this project. The time period was unspecified. However, the investment totalled more than $1 million, which shows a commitment from Quantstamp and that they recognize the importance of their community.
Full automation
It’s important to note that many people believe that smart contract audits cannot be fully automated because human judgment is required to understand the logic and intent of the smart contract. For example, software can spot bugs that cause the contract to not function, but it cannot detect that the wrong formula is being used to calculate the payoff of a smart contract, or detect errors that cause coins/tokens to be sent to the wrong person.
Proof-of-Caring (PoC)
Quantstamp also announced plans for version 2 of their proof-of-caring concept, which is a new concept put forward that rewards the community for showing they care and understand about the project by encouraging research about Quantstamp. This concept was originally established before the presale and has gained a strong following, increasing their Telegram members count from 1,000 to 14,000 members in a short period. It has not yet been announced what will be involved with version 2. However, it will run along the same lines.
How to Buy Quantstamp (QSP)
Quantstamp tokens can currently be bought on popular cryptocurrency exchanges including:
- Kucoin
- Binance
- Huobi
- Gate.io
- EtherDelta
- CoinSpot
How to Store Quantstamp (QSP)
Quantstamp token (QSP) is an ERC-20 token. This means that it can be safely stored on any ERC-20 compatible wallets. Our favourite option is MyEtherWallet. This wallet can be downloaded via the link below:
Download Quantstamp Wallet HERE (MyEtherWallet)
Check out the video below for instructions on how to download and install this wallet.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are an essential part of the ICO ecosystem, and $3.2 billion are locked into smart contracts on the Ethereum network. This number will continue to grow as more and more smart contracts are deployed. The company is still early-stage with its founding in June 2017, but with the successful Request Network audit they have shown that they are progressing at a fast pace.
Currently, the cost of auditing smart contracts starts at $5,000 and standard times are weeks to months to do an audit. Quantstamp aims to build a protocol to quicken and automate the process and it is tackling this issue by trying to reduce both the price and the time needed, to about $10 and finishing the audit within minutes respectively.
To conclude, it is clear there is a need for securing smart contracts and Quantstamp is providing a very reasonable solution.