On CoinMarketCap there are currently 208 crypto exchanges listed, where exchanges with no fees are excluded. When no fees are being charged at the exchange, it is possible for a trader (or bot) to trade back and forth with themselves and generate a lot of “fake” volume without penalty. It’s impossible to determine how much of the volume is fake so they excluded it entirely from the calculations.
Due to the large number of exchanges and high volatily of cryptocurrencies, traders can take advantage in the form of arbitrage.
An arbitrage is the possibility of a risk-free profit after transaction costs. For example, an arbitrage is present when there is the opportunity to instantaneously buy something for a low price and sell it for a higher price. People who engage in arbitrage are called arbitrageurs, such as a bank or brokerage firm. The term is mainly applied to trading in financial instruments, such as bonds, stocks, derivatives, commodities and currencies.
With so many exchanges available, there could be the same asset but with different price on different exchange. For instance, the price of an asset A on exchange 1 is 10$, while on exchange 2 it is 15$.
What you'll learn 👉
Types of Arbitrage
If you are planning to start arbitrage trading, you should be are that it is possible when one of three conditions is met:
– The same asset does not trade at the same price on all markets (“the law of one price”).
– Two assets with identical cash flows do not trade at the same price.
– An asset with a known price in the future does not today trade at its future price discounted at the risk-free interest rate (or, the asset has significant costs of storage; as such, for example, this condition holds for grain but not for securities).
There are three types of arbitrage:
– Simple arbitrage: Where cryptocurrencies are traded on more than one exchange, arbitrage occurs by simultaneously buying in one and selling on the other.
– Triangular arbitrage: arbitrage resulting from a pricing discrepancy among three different currencies in the foreign exchange market. A triangular arbitrage strategy involves three trades, exchanging the initial currency for a second, the second currency for a third, and the third currency for the initial. For instance, buying Ethereum in EU, sell the Ethereum in the Japan, and then exchange the Japanese Yen back into euro for a profit.
– Price convergence arbitrage: As a result of arbitrage, the price of cryptocurrencies in different markets tends to converge. For instance, the price of Ethereum at Kraken exchange is $1.000, and the price of Ethereum at Bitstamp exchange is $1,500. The price at Kraken is undervalued and the price at Bitstamp is overvalued. Arbitrageurs can buy Ethereum at Kraken and sell the Ethereum at Bitstamp. Due to the effect of price convergence, the prices will become more equal. Your profit will be the amount of convergence.
Risks Inherited With Arbitrage Trading
Before you start making your arbitrage strategy, you should consider risks related to arbitrage trading.
Execution Risk – As a rule, it is impossible closing two or three transactions at the same time. This raises the possibility that when one part of the deal is closed, a quick movement in prices makes it impossible to close the other at a profitable price.
Additionally, if you are trying to profit from price difference between Bitcoin on the Kraken exchange and Bitcoin on the Bitstamp exchange, you could buy a large amount of Bitcoin on Kraken and just to find that you cannot simultaneously sell on the Bitstamp.
Counterparty Risk – By definition it is a risk that counterparty fails to fulfill their side of a transaction. This is a serious problem if one has either a single trade or many related trades with a single counterparty, whose failure thus poses a threat, or in the event of a financial crisis when many counterparties fail. This hazard is serious because of the large quantities one must trade in order to make a profit on small price differences.
In order to execute your arbitrage strategy, you will need to store your coins on exchange. One of the main rules of the crypto security is not to store your assets at exchanges. There has been numerous hackings of exchanges were customers lost their money.
The solution would be to trade on decentralized exchanges, but for the purpose of arbitrage you need high liquid exchanges and liquidity on decentralized exchanges are very low for now.
Liquidity Risk – It is a financial risk that for a certain period of time a given financial asset, in our case cryptocurrency, cannot be traded quickly enough in the market without impacting the market price.
If you want to successfully apply your arbitrage strategy, the market must be liquid. If the market is not liquid, it means that you cannot execute your planned transaction without a significant loss and therefore you are not able to make profit on given opportunity.
Asset Transfer Risk – it is a risk of transferring your assets from exchange to another in order to make profit from arbitrage. When you spot an arbitrage opportunity, you will buy assets on exchange A and sell it at exchange B. To be able to do so, you will need to transfer purchased assets on exchange A to exchange B. For many reasons the transfer could be delayed or declined and you could miss the arbitrage opportunity.
Users have stated many problems while transferring funds from one exchange to another, here is to name a few:
– Funds could not be transferred due to blockchain going offline
– Transaction being delayed for days, due to exchanges paying low transaction fees and not thus being low on miners’ to do list
– Multiple transactions is short period of time could be transferred as one transaction
– Wallets crashing, wallets unable to sync with blockchain etc.
Risk of depreciation – It is a risk that the cryptocurrency’s price will decrease. For instance, you have made a profit from Bitcoin arbitrage trading. Just after, the price of Bitcoin starts to decline eating all your profits or even more.
The “Binance Listing Effect”
Binance (Binary + Finance = Binance) is purely crypto exchange. It means you cannot trade fiat currencies such as EUR, USD or GBP. According to their white paper, Binance matching engine is capable of sustaining 1.4 million orders per second, making Binance one of the fastest exchanges in the market today.
According to CoinMarketCap, Binance is the largest crypto exchange in the world with more than $1.5 billion daily trading volume. Binance has 338 trading pairs.

If you want to list your coin on Binance you will need to fill out a form found on their official web site. For listing tips, you can check Linkedin profile of Binance’s CEO Changpeng Zhao. According to his post, coin’s CEO/founder must fill the Binance listing request form. The rules are strict, if you don’t hear from them after you submit the form, that’s the norm in 99% of the case. You should review your submission and submit it again with more conceiving info. Only if your project passes their initial review, someone from Binance will be in touch. They are looking for good coins, with large user base, proven product and well-known team.
Binance does not accept teams who publically speculate on price or make predictions or forecasts on their token’s price. Teams are not allowed to disclose they will get listed on Binance until their coin starts trading. If this info leaks out, they will out the listing on hold, possibly indefinitely. The teams are only allowed to announce that Binance application is in progress.
The reasons for this are that most projects get a few times multiple in value after they list on Binance. It is an opportunity for arbitrage.
Latest example can be seen when Skycoin (SKY) was listed. On May 24, 2018 Binance announced that they will open trading for SKY/BNB, SKY/BTC and SKY/ETH trading pairs at 2018/05/24 09:00 AM (UTC).
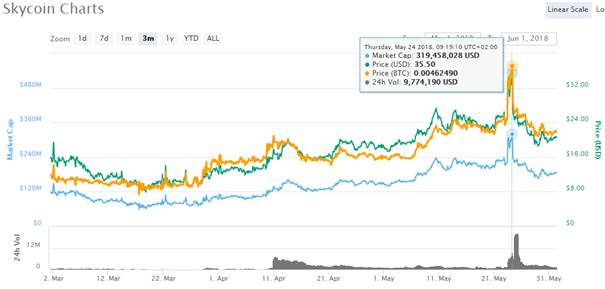
As you can see on the chart from CoinMarketCap, after getting listed on Binance Skycoin rocketed in price. On May 20, the price of SKY was $23,52 with the market capitalization of $211 million, while on the day of listing the price went up to $35,50 with the market capitalization of above $319 million.
It was a good arbitrage opportunity. If you saw the potential for SKY to get listed on Binance, you could buy SKY on exchanges such as Cryptopia before the listing. Once the SKY started trading on Binance, the buyers on Binance came flooding in. Being an owner of SKY coins already, you had to transfer your assets to Binance and sell it and make some quick profits via arbitrage.
Conclusion
The arbitrage trading can be very profitable if you are able to execute it properly. As it was stated above, the arbitrage trading carries all different kinds of risk, execution risk, counterparty risk, liquidity risk, asset transfer risk and risk of depreciation.
Basically, it all comes down to speculation as you are betting that you will be able to purchase digital coin on one exchange and them sell it higher on second exchange simultaneously and make some easy money.
If you are executing the Binance listing effect, you are also speculating as there is no guarantee that a specific coin will get listed.






