You may have heard about blockchain oracles if you have been following the technology behind smart contracts and the blockchain recently. These are indeed relatively new concepts that are most applicable to smart contract technology, so in today’s article we want to explain you their ins and outs.
What you'll learn 👉
What Are Blockchain Oracles?
An Oracle is an agent that is able to interact with the world outside the blockchain in order to find and verify real-world occurrences and submits this information to a blockchain to be used by smart contracts.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts written in code and existing on blockchain. Smart contracts contain value. However, they only unlock that value if certain pre-defined conditions are met. Once a particular value is reached, the smart contract will change its state and execute the programmatically predefined algorithms. This will automatically trigger an event on the blockchain.
However, things get a bit complicated when a smart contract is required to get information about events from outside the blockchain, because due to blockchain’s particular features, smart contracts are not enabled to connect to off-chain resources on their own, and this creates obstacles. The only way this issue can be resolved is by means of oracles.
? Wonder what is the safest wallet for BTC? Click here to find out.
The primary task of oracles is to provide the necessary data to trigger smart contracts to execute when the original terms of the contract are met. For example, an oracle could be an app that provides such input as the price of a currency, payment completion information, the weather at a given location, the result of a sport event or an election, etc.
Oracles are part of multi-signature contracts where for example the original trustees will sign a contract that will only execute or release the funds after all of those conditions have been met. It’s important to note that an oracle has to sign the smart contract as well before any funds get released.
Oracles are essential to the functioning of the smart contracts, as without them, smart contracts and therefore decentralized apps can’t run. They provide essential inputs for all of these smart contracts and allow for the legitimate interaction of these contracts with real world and external factors, and without access to these sources of information, use cases for smart contracts drop to just a tiny fraction of their potential.
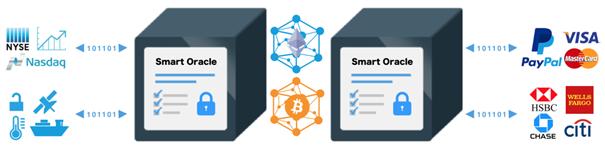
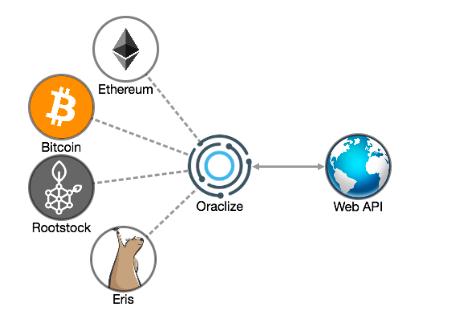
Source: smartcontract.com
Types of Oracles
Below are a few examples of Oracle solutions based on the type of use:
- Hardware Oracles – Some smart contracts need information directly from the physical world and they are designed to execute when certain conditions have been met. For example, a car crossing a barrier (marked in latitudes and longitudes) where movement sensors must detect the vehicle and send the data to a smart contract. Another use case is RFID sensors in the supply chain industry that could help the blockchain tracks the supply, for example when a product has crossed a certain stage or when a ship has landed at a particular port. The biggest challenge for hardware oracles is certain worries about data security. Oracalize, a FinTech company providing a ‘reliable connection’ between distributed apps, proposes a two-step solution to the risks, by providing cryptographic evidence of the sensor’s readings and anti-tampering mechanisms rendering the device inoperable in the case of a breach.
- Software Oracles – Software Oracles will handle all information available online on the internet required by the smart contract. An example could be weather conditions, asset prices, flight information, etc. The Oracle will gather this information through online sources, like company websites, APIs, and then send it to the smart contract.
- Inbound Oracles – Inbound Oracles provide the smart contract with data from the external world, for example a payment in Bitcoins to the supplier when the goods have been marked as delivered.
- Outbound Oracles – Outbound Oracles provide smart contracts with the ability to send data to the outside world, for example letting hotels’ intelligent lockers unlock themselves as soon as a person pays for a night.
?Searching for best best wallet for ripple? Check this out.
- Consensus Based Oracles – Some prediction markets like Augur and Gnosis rely heavily on oracles to fetch data for markets they create. Using only one source of information could be unwise in this age of information technology. Consensus Based Oracles are mainly needed for events where the data are not widely and reliably provided on the internet, and when a smart contract relies on information from a number of different sources, this is where consensus based Oracles are best used. For instance, with prediction markets, where bets are placed on how accurate a prediction might be, it is extremely important that the information of the event is 100% correct and that it comes from a number of different sources. Prediction markets implement a rating system for oracles in order to avoid market manipulation. Also, a combination of different oracles may be used for further security. For example, 3 out of 5 oracles could determine the outcome of an event.
Conclusion
Oracles are third party services with a centralized point of control, and they are not part of the blockchain consensus mechanism. The main challenge with oracles is that the source of information needs to be trustworthy because in case of mistakes there are no rollbacks. Different trusted computing techniques should be developed and used in order to solve these problems.
For example, Oracalize, which is one of the leading companies that are developing Oracle solutions at the moment, has recently developed an Oracle that would allow someone to check whether their digital identity is linked to a particular Ethereum address. Town Crier (TC), another company, is focusing on the utilization of the Software Guard Extensions (SGX), Intel’s recently released trusted hardware capability, to provide a strong guarantee that data comes from an existing, trustworthy source.
With the increasing adoption and interest in Ethereum based smart contracts, the need for new oracle structures will also rise as the structural framework that makes smart contracts possible. This will truly propel the use case for smart contracts and decentralized blockchains, and new innovations will make Blockchain-to-web communication more simple and elegant.






