
Ontology is a new high-performance, public blockchain-based project which combines a distributed identity system, distributed data exchange, distributed data collaboration, distributed procedure protocols, distributed communities, distributed attestation, and various industry-specific modules to create an infrastructure for a cross-chain, cross-system, cross-industry, cross-application, and cross-device peer-to-peer trust ecosystem. Such a decentralized, open and standardized platform will be suitable for implementation in many industries, allowing various companies to create a user friendly, interactive and blockchain-based environment for their business.
What you'll learn 👉
Trust-based network
The key element of the Ontology network is trust. Trust is a known driving force in every walk of life, from social communication to business collaboration and organization. Trust has historically manifested itself through three different lenses:
- Trust in Technology
Technologies like cryptography, biological devices, and big data are being used to build trust across industries. Blockchain technology has brought the element of trust to a whole new level and has fundamentally changed the future of trust ecosystems. Ontology utilizes this technology to create an environment where trust is enforced by the invulnerability of the blockchain itself.
- Trust in Legal Systems
The oldest and the most basic trust mechanism that Ontology relies on. We all know that legal systems preserve rights and protections across industries and across the world. These systems are closely tied to economic systems (who are probably the biggest beneficiaries of the blockchain technology in the world). By connecting the economic and legal systems on top of a blockchain multiple issues are addressed, including the issue of legal authentication, the issue of legal support and the issue of identification.
- Trust through Communities
Sociologists claim that community trust is naturally very hard to attain, with each person on average capable of trusting less than 100 people in their lives. However, trusting those close to us is also the most natural form of trust. However, internet and the information age have brought about a new dimension to the way we interact and build communities. Decentralized peer-to-peer networks created on top of impenetrable blockchains have created online communities much larger than traditional communities, where people trust eachother maybe even more than in public life.
Ontology’s distributed trust system will look to solve many trust-related issues that people face every day, including:
- Fragmented and constantly emerging sources of trust
- Reduced role of the individual in use of their own data and authentication of other people’s data
- Monopolization and hoarding of useless user data
- Data fragmentation which causes the non-monopolized data to lose out on value or flat out makes it unavailable for use
- Inaccurate identity verification
- Lack of security which comes with open networks that can have malicious nodes become a part of the system or with vulnerable centralized data storage/exchange systems
- Lack of trust and transparency in decentralized collaborative systems
- Lack of quality community management and moderation capabilities
- Lack of adequate reputation systems in decentralized networking
- Lack of transparency when making charitable donations
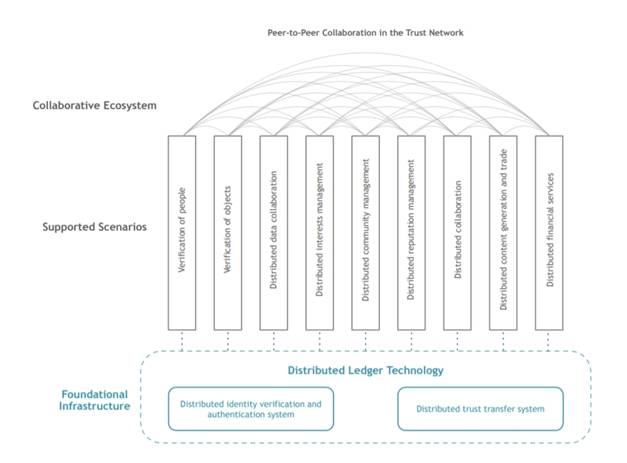
The networks multi-chain based ecosystem will help with these issues and more. It will use a system of verifiable, cryptographically protected chains to provide services like multi-source identity verification, distributed data management, and a hybrid combination of centralized and decentralized trust models.
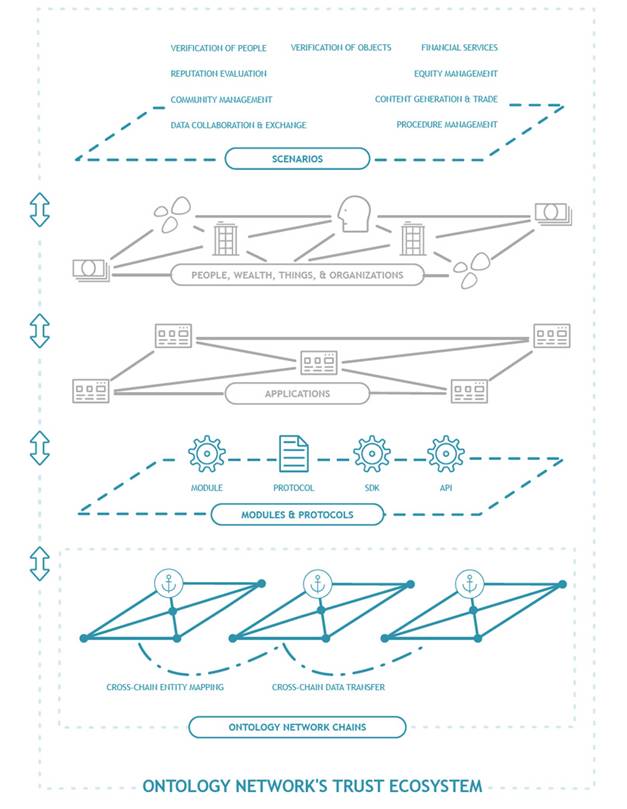
Networks multi-chain system has the following components:
- Chain 1: Verification of people, wealth, things, and organizations.
- Chain 2: Verify applications and link them together
- Chain 3: Verify and link modules, protocols, SDK’s and API’s
- Chain 4: All the different networks chains. This layer functions to link all the chains together.
By using Ontology’s trust ecosystem, companies can integrate and develop their own systems of trust on top of a decentralized ledger that includes smart contracts and security protocols. Ontology encourages trust cooperation and allows projects of all shapes, sizes, and technologies with different business scenarios and compliance requirements to pass through Ontology’s chain networks and take advantage of the distributed trust network how they see fit.
Some of the most common use cases for Ontology will include:
- Finance: Trading Securities, Wealth management, Derivatives trading, Collateral management, Supply chain finance,
- Payments: Micropayments, Business-to-business, international remittance, Tax filing and collection, Know your customer (KYC), Anti-money laundering (AML)
- Insurance: Claim filings, Claims processing and admin, Fraud detection, Telematics and ratings, Digital authentication,
- Internet of Things: Device-to-device payments, Automated operations, Grid management, Smart home management, Office management
- Consumer: Sharing economy, Supply chain, Pharmaceutical tracking, Agricultural food authentication, Shipping and logistics management
- Media: Digital rights management, Art authentication, Ad placement, Ad click fraud reduction, Resale of authentic assets
- Software Development: Micritization of work, Disbursement of work, Ad placement direct to developer payments, Ad placement API platform, Ad placement notarization and certification
- Medical: Record sharing, Prescription sharing, Multi-factor authentication, Personalized medicine, DNA sequencing
- Asset Titles: Diamonds, Designer brands, Car leasing and sales, Home mortgages, Land title ownership, Digitalization of assets
- Government: Voting, Vehicle registration, Benefits distribution, Copyrights, Education certificates
ONT technology
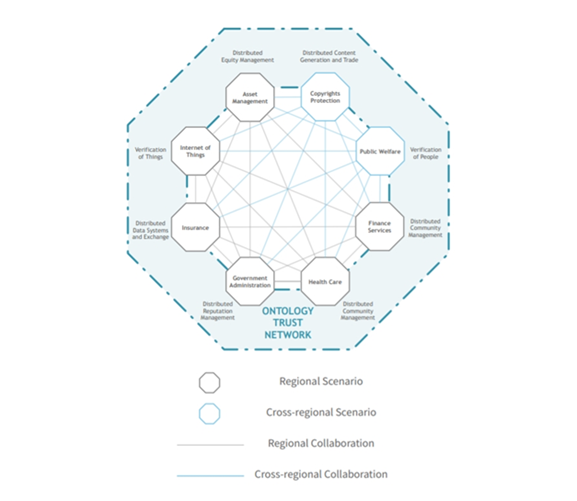
ONTs technology architecture is somewhat complicated but creates a system that guarantees digital identities and other user data is shared securely. A distributed ledger that allows for cross chain mapping and data transfer is on its bottom layer. This layer is in charge of supporting the multiple different blockchains that will be built on top of it. Core protocols which create the distributed trust framework, data protection/storage and a smart contract system are on the second layer. This level creates a framework where different industries can create their own blockchains, forming a network grid. Third layer will be the application layer made out of application modules and protocols. Ontology is able to offer a diverse set of application protocols and modules that enable developers to build decentralized applications without needing to understand the complexities of the underlying architecture. Final, fourth layer will be comprised out of data collaboration/trade, content sharing and reputation system.
The platform will be handled by a unique consensus mechanism called Ontorand Consensus Engine (OCE) which will combine Verifiable Random Functions (VRF) and a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) protocol (the engine is also named VRFT by these last two abbreviations). The engine selects the nodes that will take part in consensus voting through VRF and then lets them reach the consensus through a BFT algorithm.
ONT and NEO connection
Ontology was created by a Chinese company Onchain and was envisioned from the start as a project closely related to NEO. There has been plenty of comparison and confusion between these two projects, especially considering the fact that Ontology implements the NeoVM virtual machine. The NeoVM is highly scalable and employs a “deterministic call tree” technology that allows for dynamic sharding. While Ontology and NEO are planning to “build a broad ecosystem using blockchain and other new technologies to serve the real economy” together, the two companies are separate entities. Da Hongfei, founder of NEO, spoke on this topic in a recent interview:
“First, I need to clarify that NEO and OnChain are separate entities, so OnChain doesn’t own NEO, or NEO, OnChain. They are separately funded – NEO is funded by the community, and OnChain is funded by a very famous financial group in China, Fosun. They bought a lot of insurance companies and banks in Europe. So they are separate. Second, OnChain benefits from the NEO ecosystem. The product, called DNA, is very similar to NEO, but it is written in the Go language. OnChain is helping other blockchains and financial institutions to build their blockchains with DNA. It’s basically very similar to NEO, and in the future, with NEOx (the crosschain protocol) everything can be linked together.”
The ONT Token
The ONT token was initially airdropped to Neo holders is March 2018. 20 million tokens were distributed to the community during the airdrop. Current circulating supply is at 122.972.076 ONT tokens. The max. supply will be 1 billion tokens and it is planned to be distributed in the following way:
- 12% will go to the Ontology community
- 28% for institutional partners
- 10% to the NEO Council
- 25% to the development of the Ontology ecosystem
- 10% to Ontology technical community rewards
- 15% to Ontology core team.
The token will have Ontology GAS tokens (similar to NEOs GAS tokens) which will be paid out to holders of ONT.
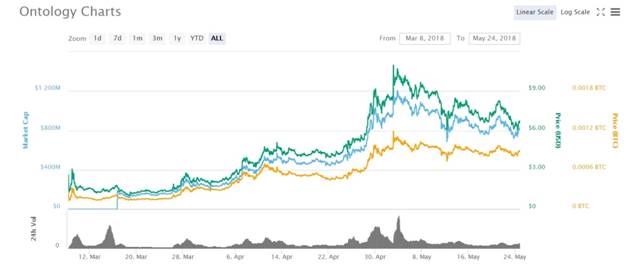
The graph looks very nice, with coin not suffering any major setbacks or bearish movements, even during the latest negative trend that the market went through. The only issue could be the max supply of 1 billion that might limit the heights ONT price will reach in the future. It can be purchased on major markets like Binance, OKEx, Huobi, Gate.io, Upbit as well as some smaller ones. For a full guide on how to purchase ONT, check out this link.
Team
Ontology was created by the Chinese company Onchain in 2017. The developers are consistently in touch with the general public through their social media and are actively encouraging freelance developers to join the process. Information on how to contribute to the project can be found on their Github page and their documentation hub.

Jun Li is the founder of Ontology and also the Co-founder of Onchain. Li has a rich academic background, including a Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science, Master’s in Communication Engineering, MBA, and PMP. He is a senior blockchain architect and blockchain solutions professional with 16 years’ work experience in IT and fintech. The rest of the Ontology Team consists of Ontology’s core team, teams of partners, community contributors, and technical contributors from around the world including personal technical contributors, technical community groups, and institutional technical contributors. Ontology’s core team is composed of experts in blockchain technology, distributed application development, product management and design, marketing and business development, and experts and architects from global financial institutions. At present there are more than 60 core team members.
Final thoughts
Ontology’s blockchain protocol wants to enable a global adoption of blockchain technology in every industry of the world. It aims to create a fully trusted platform that is universally applicable, eliminating the learning curve of designing a blockchain project from scratch and offering mass-customization. It should help solve many issues that are currently plaguing established platforms by providing some innovative new features supported by a technically advanced distributed ledger architecture. There is a lot more information available in the projects whitepapers; we recommend that you go and read those and familiarize yourself with one of the hottest projects of 2018.
- Website
- Medium
- Github
- Introductory Whitepaper
- Tech Whitepaper
- Ecosystem Whitepaper
- Documentation
- Discord
- Telegram
- Coinmarketcap





