What you'll learn 👉
Table Of Contents
Originally, blockchain was developed for Bitcoin and it was used as decentralized system for financial agreements. The blockchain technology can also be used for other transactions such as trading stock, buying and selling real estate, buying music, etc.
Many blockchains have been developed and implement in the recent time. For instance, exchange platforms are based on peer-to-peer and blockchain technology. Firstly, users need to deposit their money or tokens into an exchange’s bank account or wallet. Since user accounts will be credited an IOU. They are in fact trading their IOU on the exchange. Users have to file a ticket when they want to withdraw or sell the tokens.
In the past years, many exchanges have had problems with theft, such as „Mt. Gox“ who suspended trading, shut down its website and exchange services, and filed for bankruptcy in February 2014. They have announces that 850,000 Bitcoins were stolen from customers’ accounts, valued at more than $450 million at the time. In 2016, the Bitfinex Hack occurred in which $72 million in BTC were stolen from customer accounts. It is evident that centralized exchanges carry high level of risk due to the lack of regulation and customer protection.

This is where LoopRing idea was born. LoopRing does not require the customer to deposit or lock any asset, meaning an asset has zero third party risk. All of the transactions are made through the user’s coin address. LoopRing also changes the”Trading Pair” concept utilized by centralized exchanges. Transactions can be completed with multiple parties, rather than two parties in current exchange scenarios.
According to their white paper, here are the differences between centralized exchange and LoopRing exchange:
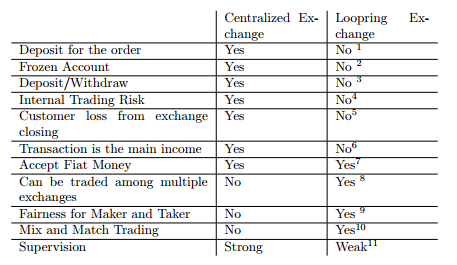
- Exchanges execute under LoopRing ecosystem does not require any deposit – Tokens are kept in user’s wallet, no transaction will be made before the full contract close. As a result, no account can be stolen, or asset lost risk.
- LoopRing exchanges do not require freeze trading fund — if a user partially or fully modifies the fund, the contract will be withdrawn automatically.
- The sender’s order can be distributed to multiple receivers to be partially or fully fulfilled under LoopRing ecosystem.
- All matching trades are based on smart contract on blockchain, data are immutable and transparent.
- LoopRing exchanges are not responsible for tokenization, thus LoopRing users will not be affected if an exchange becomes insolvent. For example, a blockchain account will not affect if mining is terminated. In conclusion, exchanges are responsible for matching trades. LoopRing’s smart contract will complete clearing and settlement; furthermore, assets are always kept in users blockchain account.
- Transaction fee is not a mainstream income for LoopRing exchanges, mainstream comes from profit of transaction margin, because it can effectively encourage trade matching.
- LoopRing exchange fully support asset tokenization, hence, it requires legitimate currency being tokenized on ERC20 standard.
- LoopRing allows multiple LoopRing exchanges to partially or fully trade off one order at same time.
- Transaction price is closed to the balance price instead of being tendered to the makers offer price under LoopRing protocol.
- LoopRing exchanges multiple supporting feature can help sender to find the most profitable order.
- LoopRing exchanges do not require a deposit. Clearing and settlement are made through the open source smart contract. Therefore, regulation is not necessary if there is no asset tokenization occurrence.
The Exchange Protocol
According to their web site, LoopRing is an open, multilateral token exchange protocol, for decentralized exchange on the Ethereum blockchain. LoopRing is intended to serve as a common building block with open standards, driving interoperability among decentralized applications (DAPPs) that incorporate exchange functionality. Trades are executed by a system of Ethereum smart contracts that are publicly accessible, free to use, and that any dApp can hook into.
The behind LoopRing was inspired by both 0x protocol and payment channel and made their own new solution for a decentralized exchange protocol.
Let’s take a look at how exactly the protocol works.
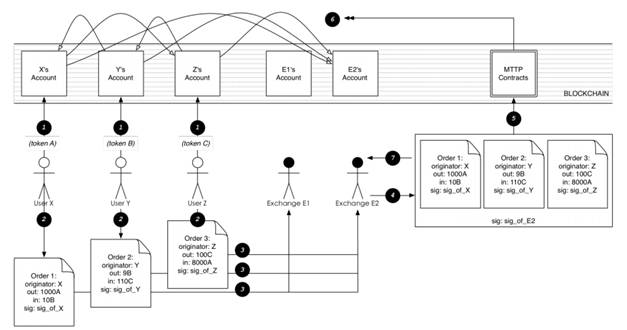
Step 1, the users have to allow the Loopring smart contract to access their accounts for token trading. As you can see from the above figure, smart contract can only transfer out 1000 A tokens from user X, 9 B tokens from user Y and 100 C tokens from user Z.
Step 2, users place orders signed with their private keys. Order 1 is selling no more than 1000 A tokens and buying no less than 10 B tokens, if the order is partially matched, then the exchange rate between tokens A to B should be no less than 1000/10=100 (number of tokens sold divided by number of tokens purchased).
Step 3, after the exchange receives all three separated orders, they will replace them into a corresponding order-book, while updating a new block and calculating each orders status to match the set order – creating a loop it will delineate as a ring exchange or matching exchange. Once all the orders are confirmed and successfully mix-matched.
Step 4, exchange will send out a signature to the given LoopRing smart contract address.
Step 5, LoopRing smart contract will verify quadruple signatures in order to verify three orders closing. If closing fails, the contract will be terminated. Loopring smart contract needs to calculate the proceeds and cost for each users, to complete the token exchange. During each step, LoopRing smart contract will use Loopring Registration Contract to calculate all the fees and discount before closing. The system will also need to use LoopRing Stats Contract to update the database. Exchange begins receiving new block and new data from the chain in order to update the order-book to mix-match new and existing orders.
Smart Contracts
LoopRing offers many smart contracts, such as:
- Mix-Matched Contract is responsible for ensuring each order status in the loop, calculating the price and volume, transferring and interaction with other smart contracts, API for Loopring;
- Order Contract updates order database and supports cancelling policy;
- Registration Contract maintains and upgrades service for exchanges who accepted Loopring, support the token deposit from exchange and defaulted parameters backup;
- Stats Contract calculates the exchange volume and price between two tokens.
Protocol Token LRC
LoopRing has its own token, based on ERC20 Ethereum Token Standard called LRC (displays in italics). The token will be used for following:
- Gas Fees — LRC can be paid as transaction fees to the exchange. It will be simple and productive for the exchange to calculate all the cost in LRC. Same as request sender and receiver.
- Deposit for Exchange Registration — the decentralized exchange mechanism has no limits on location or time. Consequently, exchanges with a high turnover would receive more orders and get more users. As a result, we have designed a policy for such exchanges that allow users to use LRC to deposit into a smart contract in order to increase the exchanges credibility. Moreover, it can also protect users from certain adverse circumstances.
LoopRing requires exchanges to provide a discount for transactions made through their protocol. The percentage of this fee can be negated by depositing LRC tokens into the protocol and the rank of the exchange determines the discount that needs to be provided.
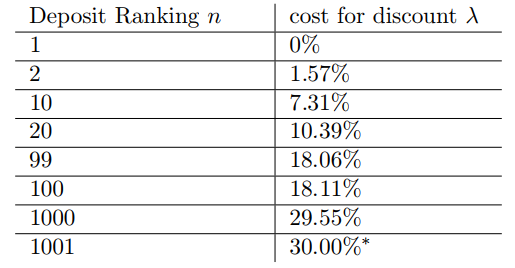
This means that exchanges will have to buy more tokens in order to increase their rankings to decrease their discount and therefore making more profits.
The Market Cap
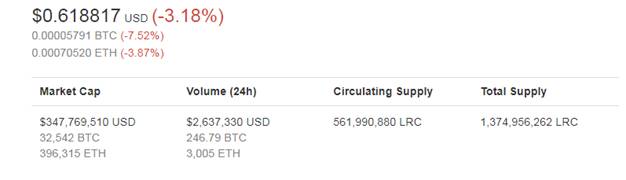
At the moment of writing, the price of LRC stands at $0.618817 with market capitalization of more than $347 million. Circulating supply is 561,990,880 tokens with total supply of 1,374,956,262.
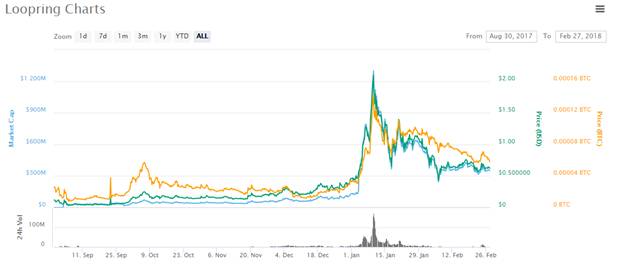
LRC reached its all-time high price of $2.09 on 10th January 2018, with market cap of close to $1.3 billion and daily trading volume of more than $172 million.
Conclusion
The LoopRing is a rare truly decentralized exchange protocol on the Ethereum blockchain. It provides unique approach to liquidity problems by allowing partial order executions with mitigated risks. The user’s funds stay on user’s wallets; you do not have to deposit funds in order to make a trade.
The user’s order can be distributed to multiple exchanges to be partially or fully fulfilled under LoopRing ecosystem. LoopRing users will not be affected if an exchange becomes insolvent.